Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) is one of the simplest yet most powerful ways to assess your overall health status. Whether you’re starting a fitness journey, monitoring your weight management progress, or simply curious about where you stand health-wise, having access to a reliable BMI calculator makes all the difference.
The challenge? Most online BMI calculators are buried under advertisements, require unnecessary personal information, or deliver confusing results without context. You deserve better—a tool that’s lightning-fast, completely private, and actually helpful.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll introduce you to the most exceptional BMI calculator available in 2025, along with trusted alternatives, so you can make informed decisions about your health with confidence.
Why This BMI Calculator Stands Above the Rest
Privacy-First Design That Protects Your Data
Your health information is personal and should remain that way. Unlike many BMI calculators that collect your data, send it to remote servers, or track your usage for advertising purposes, BMI Calculator processes everything directly in your browser.

This means:
- Zero data collection—your weight and height never leave your device
- No registration required—start calculating immediately
- Complete anonymity—no tracking cookies or user profiles
- Secure by design—your privacy is built into the architecture, not added as an afterthought
In an era where personal health data is increasingly valuable to third parties, this privacy-first approach isn’t just refreshing—it’s essential.
Lightning-Fast Calculations With Zero Loading Time
Time is precious, especially when you’re in the middle of a health check or doctor’s appointment. This BMI calculator delivers instant results the moment you input your measurements. No spinning wheels, no “processing” delays, no unnecessary steps.
The streamlined interface eliminates every possible barrier between you and your results:
- Clean, distraction-free design with no advertisements cluttering the screen
- Mobile-optimized interface that works flawlessly on smartphones and tablets
- Intuitive controls that require zero learning curve
- Responsive design that adapts to any screen size without compromising functionality
Comprehensive Results That Actually Explain What Your BMI Means
Getting a number is one thing—understanding what it means for your health is something else entirely. This calculator doesn’t just give you a BMI score and leave you wondering what to do next.
You’ll receive:
- Clear category classification: Underweight, Normal Weight, Overweight, or Obese
- Visual indicators: Color-coded results that make interpretation immediate and intuitive
- Health context: Explanation of what your BMI range typically indicates
- Actionable guidance: Suggestions for next steps based on your results
The calculator uses WHO (World Health Organization) standards, ensuring your results align with internationally recognized health guidelines.
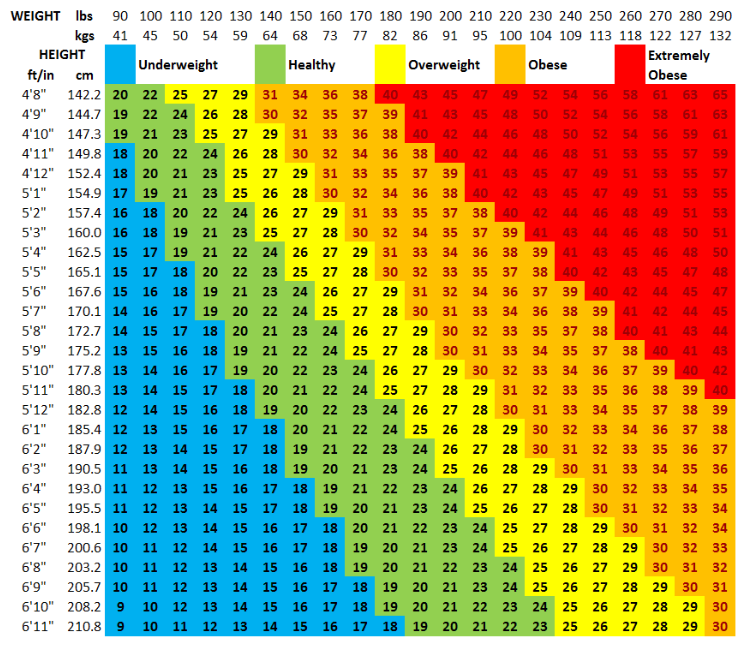
Support for Both Metric and Imperial Units
Whether you measure in kilograms and centimeters or pounds and inches, this calculator seamlessly handles both systems. Simply toggle between metric and imperial units with a single click—no mental math or online conversion tools needed.
This flexibility makes it perfect for:
- International users accustomed to different measurement systems
- Healthcare professionals working with diverse patient populations
- Travelers monitoring their health across different countries
- Anyone who prefers one system over another
Calculate your BMI now: https://bmi.zucca100.com/en
Alternative BMI Calculators Worth Considering
While the Zucca100 BMI Calculator excels in privacy, speed, and user experience, these alternative tools offer their own unique advantages depending on your specific needs.
CDC BMI Calculator – Medical Authority Standard
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers an official BMI calculator backed by extensive medical research and population health data.
Key Strengths:
- Developed by leading public health experts
- Separate calculators for adults and children/teens with age-appropriate standards
- Extensive educational resources explaining BMI limitations and context
- Regular updates based on latest health research
Best For: Users who want authoritative medical context and detailed health information alongside their calculation.
Access it here: CDC BMI Calculator
Calculator.net BMI Tool – Feature-Rich Option
This comprehensive calculator goes beyond basic BMI calculation to include additional metrics like Ponderal Index and detailed category breakdowns.
Key Strengths:
- Multiple calculation methods including BMI Prime and Ponderal Index
- Extensive charts showing BMI ranges across different demographics
- Detailed explanations of what each measurement indicates
- Historical context and scientific background on BMI development
Best For: Users interested in deeper analysis and multiple health metrics beyond standard BMI.
Try it at: Calculator.net BMI
NHLBI Calculator – Government Healthcare Standard
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute provides a straightforward, no-nonsense BMI calculator that focuses on cardiovascular health implications.
Key Strengths:
- Direct connection to heart health and cardiovascular risk factors
- Government-backed reliability and accuracy
- Simple interface without overwhelming information
- Links to related health resources and prevention strategies
Best For: Individuals specifically concerned about heart health and cardiovascular risks related to weight.
Calculate here: NHLBI BMI Calculator
Understanding Your BMI Results
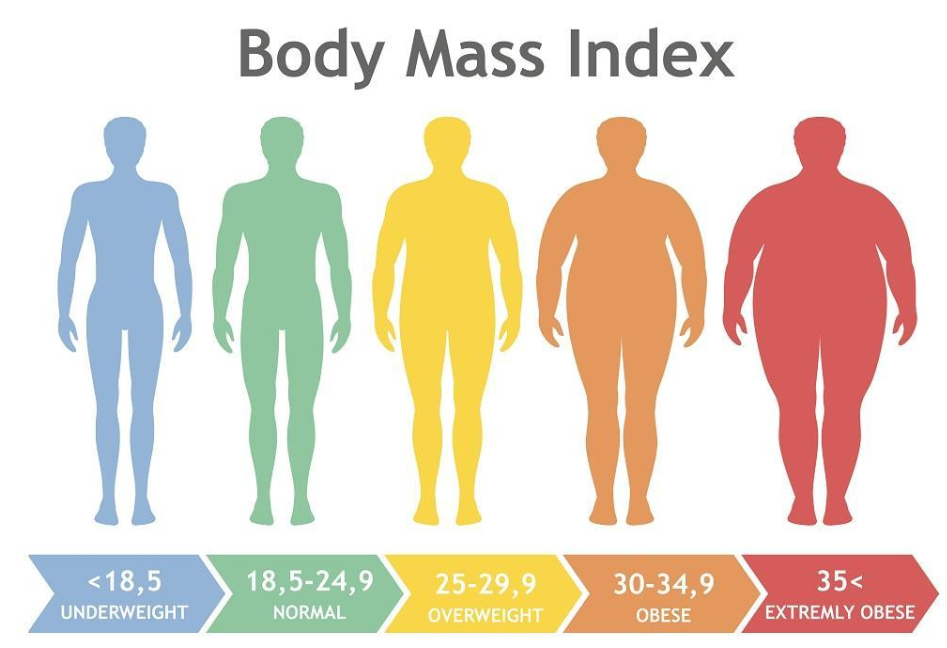
What BMI Actually Measures
Body Mass Index is a ratio comparing your weight to your height. The formula divides your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared (kg/m²), or for imperial measurements, weight in pounds divided by height in inches squared, multiplied by 703.
This calculation provides a screening tool that correlates with body fat percentage for most people, though it’s not a direct measurement of body composition.
BMI Categories and What They Mean
Underweight (BMI below 18.5):
- May indicate insufficient nutrition or underlying health conditions
- Associated with weakened immune system and reduced bone density
- Consultation with healthcare provider recommended
Normal Weight (BMI 18.5-24.9):
- Generally associated with lowest health risk from weight-related conditions
- Indicates healthy proportion of weight to height for most individuals
- Maintenance through balanced diet and regular exercise recommended
Overweight (BMI 25-29.9):
- Moderate increased risk for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension
- Often manageable through lifestyle modifications
- Consider consultation for personalized weight management plan
Obese (BMI 30 and above):
- Significantly elevated risk for serious health conditions
- Further subdivided into Class I (30-34.9), Class II (35-39.9), and Class III (40+)
- Medical supervision recommended for weight loss and risk management
Important Limitations to Consider
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it has important limitations you should understand:
Doesn’t Distinguish Between Muscle and Fat: Athletes and bodybuilders with high muscle mass may show as overweight or obese despite having low body fat percentages. Muscle weighs more than fat, which BMI doesn’t account for.
Age-Related Variations: Older adults naturally lose muscle mass and bone density with age, which can affect BMI interpretation. Some research suggests slightly higher BMI ranges (25-27) may be healthier for people over 65.
Ethnic and Racial Differences: Studies show BMI thresholds for health risks vary across populations. Asian individuals may face increased health risks at lower BMI levels (starting at 23), while the standard BMI categories may overestimate risk for Black individuals.
Not Suitable for Children: Children and teenagers require age and gender-specific BMI percentile charts rather than adult BMI categories, as their body composition changes dramatically during growth.
Pregnancy Considerations: BMI calculations don’t apply during pregnancy. Pregnant individuals should consult healthcare providers for appropriate weight gain guidance.
Doesn’t Measure Body Composition: BMI can’t tell you about your muscle-to-fat ratio, bone density, or where fat is distributed in your body—all factors that significantly impact health.
How to Use BMI Effectively in Your Health Journey
Combine BMI with Other Health Metrics
BMI works best as part of a comprehensive health assessment, not as a standalone measure. Consider tracking:
- Waist Circumference: Measures abdominal fat, which poses greater health risks than fat stored elsewhere. Men should aim for less than 40 inches, women less than 35 inches.
- Waist-to-Hip Ratio: Another indicator of fat distribution and cardiovascular risk.
- Body Fat Percentage: More accurate measure of actual body composition than BMI alone.
- Blood Pressure: Direct indicator of cardiovascular health regardless of weight.
- Blood Sugar Levels: Critical for diabetes risk assessment.
- Cholesterol Profile: Essential cardiovascular health marker.
Track Changes Over Time
A single BMI calculation provides a snapshot, but tracking changes over weeks and months reveals meaningful patterns. Regular monitoring helps you:
- Evaluate whether lifestyle changes are working
- Catch concerning trends early
- Stay motivated by seeing progress
- Make data-driven decisions about your health strategies
Calculate your BMI monthly and maintain a simple log of results alongside notes about your diet, exercise, and overall wellbeing.
Consult Healthcare Professionals for Personalized Guidance
BMI calculators provide valuable information, but they can’t replace professional medical advice. Your doctor or registered dietitian can:
- Interpret your BMI within the context of your complete health profile
- Account for individual factors that BMI doesn’t capture
- Recommend appropriate interventions based on your specific situation
- Monitor your progress and adjust recommendations as needed
- Screen for underlying health conditions affecting weight
Actionable Steps After Calculating Your BMI
If Your BMI is in the Normal Range
Congratulations! Your weight appears proportionate to your height. To maintain this healthy status:
- Continue balanced nutrition: Focus on whole foods, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats
- Stay physically active: Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly
- Monitor regularly: Check your BMI quarterly to catch any changes early
- Maintain healthy habits: Prioritize sleep, stress management, and hydration
If Your BMI Indicates Underweight
Being underweight can be as concerning as being overweight. Take these steps:
- Consult a healthcare provider: Rule out underlying medical conditions
- Increase caloric intake gradually: Focus on nutrient-dense foods rather than empty calories
- Strength training: Build muscle mass through resistance exercises
- Address potential causes: Stress, digestive issues, or eating disorders may require professional support
If Your BMI Shows Overweight or Obesity
Don’t panic—small, sustainable changes can make significant differences:
- Start with realistic goals: Losing just 5-10% of body weight can dramatically improve health markers
- Focus on behavior, not just numbers: Develop sustainable eating and activity patterns
- Seek professional support: Dietitians, personal trainers, and physicians can provide evidence-based guidance
- Address root causes: Emotional eating, stress, sleep deprivation, or medications may contribute
- Consider medical evaluation: Check for conditions like hypothyroidism, PCOS, or insulin resistance
The Science Behind BMI
Historical Development
Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet developed the BMI formula in the 1830s as a way to study population-level obesity trends. Originally called the “Quetelet Index,” it wasn’t intended for individual health assessment but rather for large-scale statistical analysis.
The medical community adopted BMI in the 1970s as a practical screening tool because it requires only height and weight—measurements easily obtained in any clinical setting without expensive equipment.
Why Healthcare Still Uses BMI
Despite its limitations, BMI remains valuable in healthcare for several reasons:
- Strong population-level correlations: BMI accurately predicts health risks when examining large groups
- Cost-effective screening: Requires no special equipment or training
- Quick assessment: Provides immediate feedback in clinical settings
- Research standardization: Allows comparison across studies and populations
- Insurance and policy applications: Provides consistent criteria for healthcare decisions
Emerging Alternatives and Complements
Medical research continues developing more sophisticated measures:
- Body Adiposity Index (BAI): Uses hip circumference and height to estimate body fat percentage
- Waist-to-Height Ratio: Simple calculation that some research suggests better predicts cardiovascular risk
- DEXA Scans: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry provides precise body composition analysis
- Bioelectrical Impedance: Estimates body fat percentage using electrical signals
Common BMI Myths Debunked
Myth: BMI Applies Equally to Everyone
Reality: BMI standards were developed primarily from European populations and may not apply universally across all ethnic groups. Asian health organizations use lower thresholds (overweight at 23, obese at 25) based on research showing increased health risks at lower BMI levels in Asian populations.
Myth: A High BMI Always Means You’re Unhealthy
Reality: While high BMI correlates with increased health risks at the population level, individuals can be metabolically healthy at higher BMIs, particularly if they’re physically active and have favorable blood markers. Conversely, some people with normal BMI have poor metabolic health.
Myth: BMI Can Determine Your Ideal Weight
Reality: BMI provides a range, not a specific target. Your ideal weight depends on numerous factors including muscle mass, bone density, genetics, and overall health status. Two people with identical BMIs can have vastly different body compositions and health outcomes.
Myth: You Should Aim for the Lowest Possible BMI
Reality: Being underweight (BMI below 18.5) carries health risks including weakened immunity, osteoporosis, fertility issues, and increased mortality risk. The goal is finding your optimal healthy range, not minimizing the number.
Make BMI Calculation Part of Your Routine
Knowledge is power when it comes to your health. Regular BMI monitoring provides valuable data that, combined with other health metrics and professional guidance, empowers you to make informed decisions about your wellbeing.
The key is choosing tools that respect your privacy, deliver accurate results, and provide meaningful context—exactly what the BMI Calculator offers.
Your Action Plan
- Calculate your current BMI using a reliable, privacy-focused calculator
- Record your result along with the date for future comparison
- Assess your result honestly considering the limitations and context we’ve discussed
- Set realistic health goals if changes are needed
- Schedule regular check-ins monthly or quarterly to track progress
- Consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance based on your complete health profile
Remember: BMI is a screening tool, not a diagnosis. It’s one piece of information in the larger puzzle of your health. Use it wisely, understand its limitations, and always consider the bigger picture of your overall wellbeing.
Start your health assessment today: Calculate Your BMI Now
Your health journey begins with understanding where you are today. Armed with accurate information and the right tools, you’re already taking important steps toward a healthier future.
益群网:终身分红,逆向推荐,不拉下线,也有钱赚!尖端资源,价值百万,一网打尽,瞬间拥有!多重收益,五五倍增,八级提成,后劲无穷!网址:1199.pw
又到年底了,真快!